Describe the Wavelength of a Longitudinal Wave
There are two basic types of wave motion for mechanical waves. Lets take a look at how they differ.

10 Differences Between Longitudinal And Transverse Waves With Examples Similarities Viva Differences
Turn on Show rulers.

. 2 they carry and transfer energy. 5 rows What Is Longitudinal Wave. The wavelength of a longitudinal wave can be measured as the distance between two adjacent compressionsFeb 19 2021.
The wavelength of a longitudinal wave is equal to the distance between two. A perpendicular wave is a type of wave whose direction is transversal to the direction of movement of the wave. Describe how you could measure the amplitude of a transverse wave.
Describe two ways you could measure the wavelength of a longitudinal wave. A point on any coil of the spring will move with the wave and return along the same path. In air at 42 degrees f.
4 light waves but not sound waves. The wavelength of a longitudinal wave is defined as the distance between two consecutive points. The wavelength of a 10 Hz.
921 Acoustic propagation wave theory. From left to right. 92 Compression and rarefaction ESACT.
With the lights on click Pause. Physics 02092019 1830 mannster03. In a longitudinal wave the motion of the medium is parallel to the direction of the.
Y is the displacement. In the case of longitudinal harmonic sound waves the frequency and wavelength can be described by the formula where. We usually take these two points as two compressions or two rarefactions but the wavelength can be measured between any two in phase points.
The oscillations in pressure are sinusoidal in nature and are characterised by their frequency amplitude and wavelength Figure 91. Aim of the experiment. In general a low pitch low frequency will have a long wavelength.
The wavelength in a longitudinal wave is the distance between two consecutive points that are in phase. The properties of perpendicular waves and longitudinal waves include amplitude frequency period and wavelength. Wave is 110 feet.
Sound waves are longitudinal waves. Wavelengths in longitudinal waves are measured by the distance between contractions or rarefactions therefore your could use time as a measurement or distance. Particles of the fluid ie air vibrate back and forth in the direction that the sound wave is moving.
8 waves with a short wavelength have a high frequency and high energy. Longitudinal waves are the waves where the displacement of the. The wavelength of a 1 cycle per second frequency is 1100 feet.
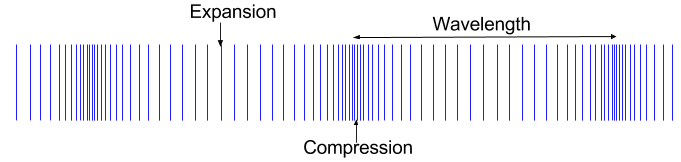
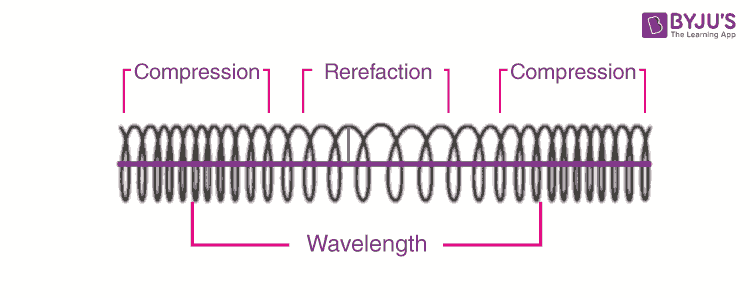
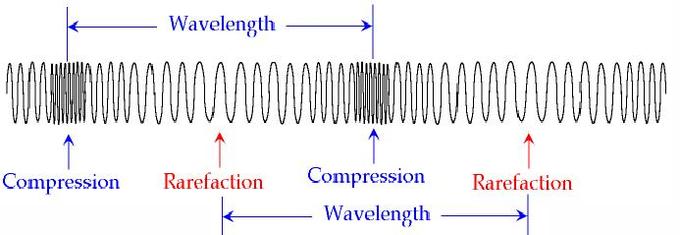
Longitudinal and Transverse Wave Motion. The wavelength refers to the distance between two consecutive compressions or between two consecutive rarefactions. The wavelength in a longitudinal wave refers to the distance between two consecutive compressions or between two consecutive rarefactions.
A coiled spring that is compressed at one end and then released experiences a wave of compression that travels its length followed by a stretching. The wavelength of a longitudinal wave denoted by latexscriptsize lambdalatex is the distance between two consecutive points that are in phase see figure 6. The wavelength of a transverse wave can be measured as the distance between two adjacent crests.
Describe the wavelength of a longitudinal wave. Set up the ripple tank as shown in the diagram with about 5 cm depth of water. In conclusion both longitudinal and transverse waves have amplitude frequency period and wavelength whereas only.
5 an echo of sound in a canyon. Measure the distance between adjacent compressions or rarefactions. Mechanical Waves are waves which propagate through a material medium solid liquid or gas at a wave speed which depends on the elastic and inertial properties of that medium.
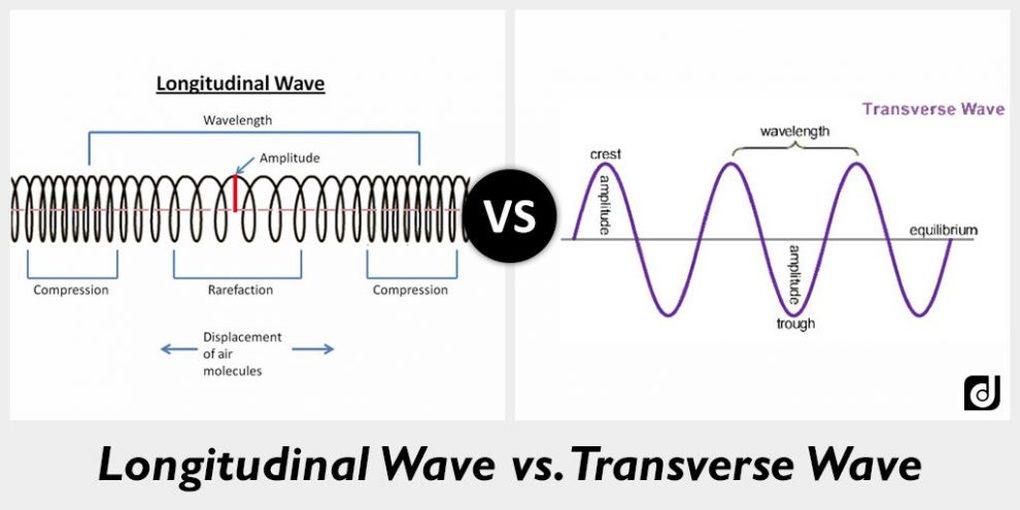
Waves may be transverse or longitudinal. In a transverse wave the medium or the channel moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave. L vf where l is wavelength v is the speed of sound and f is the frequency.
For longitudinal waves the vibration of the particles of the medium is in the direction of wave propagation. 3 a transverse wave where particles move perpendicular to the wave. Sound waves traveling through a fluid such as air travel as longitudinal waves.
Longitudinal wave wave consisting of a periodic disturbance or vibration that takes place in the same direction as the advance of the wave. The wavelength in a longitudinal wave is the distance between two consecutive points that are in phase. So each point of the spring moves back and forth as the wave is transmitted.
A compression is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are closest together. This back-and-forth longitudinal motion creates a pattern of compressions high pressure regions and rarefactions low pressure regions. These consecutive points lie either between two compressions or between two rarefactions.
Here the movement of the particles is from left to right and force other particles to vibrate. Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with a wide range of properties and uses. In a longitudinal wave the medium or the channel moves in the same direction with respect to the wave.
Velocity v Frequency f x Wavelength λ Longitudinal and transverse waves. A rarefaction is a region in a longitudinal wave where the particles are furthest apart. However instead of crests and troughs longitudinal waves have compressions and rarefactions.
To measure the frequency wavelength and speed of waves in a ripple tank. Waves come in different forms namely longitudinal and transverse waves. Longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
1 the distance between wave crests. Measure the distance from the rest position to a crest or trough. The relationship of the velocity frequency and wavelength of a wave can be described by the following formula.
Longitudinal or compression waves are defined as waves where the particle motion is in the same direction in which the wave is propagating.

Longitudinal Wave An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
What Is A Longitudinal Wave Diagram Quora

Longitudinal Wave Ck 12 Foundation

Longitudinal Wave Ck 12 Foundation

Waves Amplitude Period Frequency Wavelength Crests Troughs Wavelength Of A Longitudinal Wave Youtube

Longitudinal Wave Gobbler Courses
Wave Characteristics Review Article Khan Academy

Wave Amplitude Ck 12 Foundation

Longitudinal And Transverse Waves Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
Longitudinal Wave Definition Examples Formula Diagram

What Type Of Wave Is Sound Pasco Blog Pasco

Longitudinal Wave Definition Examples Formula Diagram

Characteristics Of Longitudinal Wave Qs Study

Longitudinal Waves Derived Copy Of Physics Grade 10 Caps 2011 Openstax Cnx



Comments
Post a Comment